A carotid artery stent is a treatment done to restore blood flow to narrow or blocked carotid arteries, which are located on either side of your neck and supply blood to your head, face, and brain. In some people the carotid arteries may become narrowed due to atherosclerosis (“hardening of the arteries”). The buildup of plaque (hard cholesterol deposits) inside the carotid arteries can lead to severe narrowing or even complete blockage. Also, pieces of plaque can break off and block an artery downstream in the brain, causing a stroke.
When doctors detect carotid artery disease (stenosis or narrowing), they may recommend the placement of a stent. A stent is a metallic, mesh-like sleeve that can be placed in the narrowed part of the artery. When expanded into place, the stent helps prop the artery open and can decrease the risk of stroke.
Lifestyle modification
To prevent further progression of carotid artery disease, lifestyle modification is recommended to limit all risk factors for coronary and carotid artery disease. These include:
- Quit smoking and using tobacco products
- Control high blood pressure and diabetes
- Have regular check-ups with your doctor
- Have your doctor check your lipid profile and get treatment, if necessary to reach a lipid goal LDL less than 100 and HDL greater than 45
- Eat foods low in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Achieve and maintain a desirable weight
- Exercise regularly
- Control other stroke risk factors: limit the amount of alcohol you drink and, if you have atrial fibrillation, you should be on blood-thinning medications
- Talk to your doctor about circulation problems that may put you at risk for stroke
Medications
Blood-thinner (anticoagulant) medications – all patients with carotid disease should be on aspirin to decrease the risk of stroke due to blood clots. In some cases, Coumadin (warfarin) or other blood thinners may be prescribed. If so, blood work may need to be checked regularly to ensure you are on the proper dose. Please see your doctor for a consultation regarding your treatment, never self-medicate.
Procedures
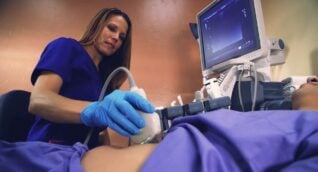
Option #1 – Carotid Artery Stenting
Carotid stenting is a minimally invasive interventional procedure that has been approved by the FDA. This procedure should ONLY be done by qualified physicians.
Drs. Conrad and Rutledge are fellowship trained to perform carotid artery stenting procedures. Make sure any doctor performing the procedure has been fellowship trained in carotid stenting and certified by the ASITN (the governing body for carotid stenting). Only qualified physicians are certified by the ASITN, if your physician is not certified by the ASITN you can contact the ASITN to refer you to a local physician who is certified. http://www.asitn.org.
Option #2 – Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy is the traditional surgical treatment for carotid artery disease. While the patient is under general anesthesia, a 3-inch incision is made in the neck, at the location of the blockage. The surgeon opens the carotid artery and removes the plaque and diseased portions of the artery. Then, the artery is sewn back together to allow blood flow to the brain. Patients are usually sent home from the hospital within a few days. Sutures from the neck incision are removed within one week.
- At the beginning of the procedure, one of ARA’s neurointerventional surgeons will make a small puncture in the thigh.
- A specially designed catheter is inserted into an artery in the thigh and directed to the area of narrowing in the carotid artery.
- Once the catheter is in place, a small balloon tip is inflated for a few seconds to dilate the artery.
- Then, a stent (a small mesh tube that acts as a scaffold to provide support inside the artery) is placed in the artery and is opened to fit the artery. Tiny filters are used to capture any particles in the artery and prevent them from going to the brain and causing a stroke.
- The stent stays in place permanently. Most patients will spend one night in the intensive care unit as a precaution and return home the next day with only a Band-Aid on their thigh.
- After several weeks, your artery heals around the stent.
The FDA’s advisory committee based their April 2004 recommendation for carotid stenting approval on a comparative study called “Sapphire.” The Sapphire study compared the results of patients that had undergone carotid stenting to patients that had undergone traditional surgery. The study indicated that carotid stenting (also called carotid angioplasty) measured up to surgery and may be safer for patients who are poor surgical risks because of advanced age or health problems.
The 310 patients in the random arm of the study were divided into two groups; 159 got stents, and 151 had surgery. The results over the next year are as follows:
| Carotid Stenting | Surgery | |
| Patients that had strokes | 5.8% | 7.7% |
| Patients that had heart attacks | 2.5% | 8.1% |
| Patients that died | 7% | 12.9% |
 Back to Top
Back to Top